Jan 13, 2025
Discover how to optimize industrial processes with digital twins and predictive maintenance to reduce costs, avoid downtimes, and improve operational efficiency.
In 2024, the manufacturing sector faced numerous challenges that tested its resilience and adaptability. The high costs of raw materials and other unpredictable economic factors wreaked havoc on many companies.
According to Siemens' report "The True Cost of Downtime 2024", unplanned downtime has had a substantial economic impact on the manufacturing sector. In the automotive sector, for example, the cost of keeping a production line idle in a large plant amounts to $695 million a year, which is 1.5 times higher than it was five years ago. Even more shocking, losing just one hour of production in this sector results in a loss of up to $2.3 million, equivalent to more than $600 per second.
These figures not only reflect the direct impact on your company's balance sheet, but they also jeopardize long-term competitiveness and stability. If you have already identified bottlenecks and inefficiencies in your processes, now is the time to take the next step: implement effective solutions that transform these opportunities into tangible improvements.
Challenges in Process Optimization: The Cost of Inaction
Competitiveness in the manufacturing sector depends on the ability to adapt to changes, optimize resources, and ensure operational continuity. However, there are common challenges that limit performance and increase operational costs.
When something goes wrong on a production line, the repercussions can affect productivity, quality, and even financial results. According to the report from “Ambiente Plástico”, an average manufacturer faces about 800 hours of downtime per year, which is more than 15 hours per week.
These problems are universal, but the lack of action makes them even more costly. Below, we explore some of the challenges faced by manufacturing companies and how their impact can be devastating if not properly addressed:
Maintenance Errors
One of the most serious issues in today's factories is their reactive or 'repair' maintenance approach, where action is only taken when something breaks down. This approach may seem adequate in the short term, but in the long run, it results in a type of cost that, according to Siemens' report, costs the 500 largest companies in the world 11% of their revenue, amounting to $1.4 trillion, a sum equivalent to the annual GDP of a major industrial nation like Spain.
Disconnected Technologies
The lack of technological integration in the manufacturing sector remains a critical barrier to efficiency and competitiveness. Many manufacturing companies still rely heavily on disconnected Excel spreadsheets or MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) to manage critical information, such as supply chain data, purchasing, and operational performance.
This fragmented approach leads to a significant loss of critical data. The most obvious consequence of this disconnection is the generation of inaccurate analyses, resulting in incomplete or outdated information. It also increases not only resource waste but also the defect and rejection rates in production due to the lack of reliable data that could have prevented errors.
Resistance to Advanced Technology Adoption
The lack of investment in advanced tools and technologies, such as digital twins or artificial intelligence, continues to limit factories' ability to adapt to market demands and improve their competitiveness. This technological delay hinders innovation and complicates the implementation of strategies that optimize both productivity and the quality of the final product.
Despite advancements, many companies have still not been able to effectively leverage technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) or augmented reality. According to the State of Mind Report by Fictiv, 88% of respondents had already implemented AI in their manufacturing and supply chain operations, but less than half achieved significant results: only 43% rated the value provided as "high," while 41% considered it "minimal." This demonstrates that implementing advanced technologies without a clear strategy does not guarantee results.
For these tools to be effective, it is important to first identify the specific needs of the factory and then choose solutions that align with those objectives. Otherwise, the inappropriate use of these technologies can create more problems than benefits, wasting resources and time in the process.
Quality Management and Regulatory Compliance
In the manufacturing sector, non-compliance with regulations has serious consequences, such as legal sanctions, significant fines, and loss of operating licenses, jeopardizing the financial stability of companies. Additionally, the impact on reputation can lead to the loss of customers and business opportunities, directly affecting revenues.
Traditionally, techniques such as Statistical Process Control (SPC) have been widely used along with tools like Excel and MES to maintain product quality. However, traditional control charts have proven to be ineffective at detecting small or moderate changes in the mean and variation of the process. This increases the risk of producing defective batches, which not only compromises quality but also exposes companies to costly regulatory interventions.
How to Address These Challenges
Traditional solutions fail to effectively address the current challenges in the sector. Often, companies must resort to multiple tools to address specific issues, exacerbating data fragmentation and complicating a unified view of their operations. These solutions also tend to generate incompatibilities with existing systems, limiting their adoption and effectiveness. TOKII addresses all these problems with its modular approach and capability to integrate advanced technologies such as Big Data and Machine Learning, enabling companies to analyze and understand large volumes of data more efficiently, generating significant value in their operations.
Predictive Maintenance Solution for Factories
TOKII, with its real-time analytics capability, allows for the implementation of predictive maintenance that transforms how equipment is managed. By continuously monitoring overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and keeping detailed track of machinery wear, it allows for anticipating unnecessary disruptions and planning interventions before failures occur. This approach significantly reduces downtime, minimizes operational costs, and improves the overall productivity of the plant.
Moreover, it includes a No-Code ML module that enables machine learning algorithms to be carried out without the need for programming, thanks to its variety of pre-trained predictive models such as forecasting, classification, and clustering, among others.
These tools allow for predictions of up to 99% accuracy, identifying patterns and optimizing maintenance operations in an agile and efficient manner.
Centralized Data System Solution
TOKII incorporates an API that allows for the easy and efficient integration of all information generated in a plant, whether from industrial machinery, IoT sensors, Excel sheets, or other data sources. The connection to these various sources is achieved through a data ingestion system with multiple adaptable plugins, such as OPC-UA, SQL, MQTT, or HTTP, ensuring a seamless and personalized integration according to each client's needs.
All processed data is visualized through an interactive digital representation that not only guarantees a comprehensive and accurate view of operations but also allows interaction with the data to make informed decisions in real-time.
By eliminating information silos and offering seamless integration, TOKII transforms data into a strategic resource, enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring that every process is aligned with business objectives.
Compliance with Regulations
TOKII has the capability to create simulated scenarios to forecast results from changes in factories concerning safety, quality, and sustainability. These scenarios can be monitored and compared in real-time with established values for regulatory compliance such as ISO 31000 and thus create risk mitigation plans.
In terms of sustainability and energy efficiency, TOKII also contributes to meeting environmental or sustainability regulations by monitoring and accounting for the carbon footprint generated during production processes.
According to the World Economic Forum, through digital twin technology, LG Electronics in Changwon (South Korea) improved productivity by 17%, product quality by 70%, and reduced energy consumption by 30%.
Digital Twins in the Manufacturing Sector
The current challenges in the manufacturing sector are complex and interconnected, ranging from maintenance management to data integration, along with the need to quickly adapt to technological advancements and ensure regulatory compliance.
However, with TOKII, companies have the opportunity to transform these challenges into competitive advantages.
We have already implemented these solutions for our clients in the manufacturing sector. Below we show you how we have done it, and the benefits they have experienced:
Success Case Vicinay Marine
Thanks to TOKII, Vicinay Marine has achieved a significant improvement in operational efficiency by reducing times and optimizing resources through real-time analysis. The ability to anticipate failures in the production line has minimized unexpected interruptions, ensuring the continuity of processes. Additionally, the system guarantees constant supervision, ensuring that all productive operations are carried out correctly.
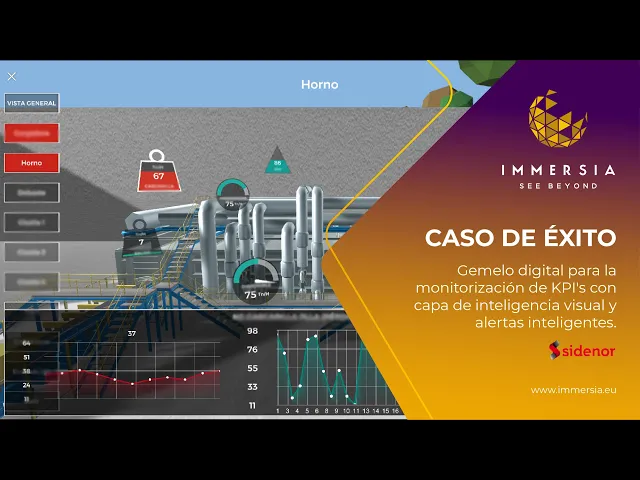
Success Case Sidenor
Through TOKII , an advanced visualization system was implemented that transformed numerical tables into intuitive and interactive visual representations. This system accelerated the interpretation of key variables such as oven temperature and early detection of operational failures.
This has allowed Sidenor to significantly improve operators' ability to react in real-time, increasing production efficiency and safety, ensuring regulatory compliance, and providing detailed analyses that support more informed strategic decisions.