
Jan 3, 2025
Discover how data, digital twins, and artificial intelligence can transform your plant into a more agile and profitable factory.
Industrial companies are becoming increasingly connected; implementing more advanced processes and more efficient machinery that generate an overwhelming amount of information. This overload of data can become an obstacle that limits efficiency and hinders growth if there is no management behind it that allows translating that data into decisions. According to the report ‘Rethink Data’ by Seagate, 68% of the data generated by companies is not utilized. This makes clear the need for many companies to have an optimization plan at the operational level. The real advantage lies not in the amount of data, but in how it is managed, analyzed, and effectively visualized. Below, we explain the role that data plays in transitioning from a “blind” factory to a “smart” factory.
Data Management: The Beginning to Transform Information into Value
Data management is a fundamental process that allows industrial companies to organize, store, and use information efficiently to extract its maximum value. In the era of Industry 4.0, data is compared to oil due to its strategic value. However, poor management can convert them into disconnected silos, significantly limiting their impact. Data management systems, such as traditional databases, data lakes, Big Data platforms, and cloud solutions, are key tools to help industrial companies overcome common problems, such as incomplete data or lack of integration between systems. One of the essential concepts within data management is Big Data, which allows processing large volumes of information in real-time, identifying patterns in production processes, and anticipating failures. However, to harness its true potential, it is crucial to complement it with analytics, which transforms data into clear insights for decision-making. With solutions like TOKII, you can integrate these technologies and practices into a platform that combines management, analytics, and advanced visualization. For example, a company can apply prescriptive analytics to adjust its production lines and reduce operational costs by leveraging patterns identified through predictive analytics.
Data Analysis: Transforming Data into Information
Data analysis is the key step that transforms information into actionable knowledge to optimize industrial operations. Analytics is classified into four types: descriptive (what has happened), diagnostic (why it happened), predictive (what will happen), and prescriptive (what to do). Each type allows understanding the past and present, forecasting the future, and defining more effective strategies.
Descriptive Analytics: Collects and analyzes historical data to understand the behavior of industrial processes and identify patterns.
Diagnostic Analytics: Delves into the causes of problems or results to propose data-driven solutions.
Predictive Analytics: Uses historical data to forecast future scenarios, enabling anticipation of errors and taking preventive measures.
Prescriptive Analytics: Combines internal and external historical data to recommend specific actions that optimize industrial processes. To implement effective data analysis, companies need tools that efficiently collect, process, and analyze data.
With TOKII, factories can integrate the capabilities of systems like SCADA, IoT platforms, and analytics software into a single solution. TOKII not only replicates physical processes virtually but also allows simulating scenarios, making real-time predictions, and offering recommendations to optimize operations.
Business Intelligence (BI): From Data to Decisions
After conducting data analysis, the next step is to transform those insights into strategic decisions. This is where Business Intelligence (BI) comes into play.
Business Intelligence (BI) is the set of tools, technologies, and strategies that companies use to collect, process, and analyze data with the aim of making more informed decisions. It helps to understand what happened, why it happened, and, most importantly, what actions to take to improve future performance.
For instance, TOKII uses Big Data to centralize, analyze, and visualize large volumes of information in real-time, connecting data from various sources. In this way, we unlock the ability to make data-driven decisions through digital twins.
Moreover, its integration with immersive technologies like augmented reality and virtual reality further enhances the understanding of data, ensuring that every decision is aligned with business objectives.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is a technique that transforms complex information into intuitive graphical representations, facilitating interpretation and informed decision-making.
Our brain processes visual information more quickly and effectively, which explains why graphical representations have been fundamental in transmitting knowledge throughout human history.
Images communicate universally what cannot be expressed through words, which is why it has become an indispensable tool for companies that handle large volumes of data. Visualization allows obtaining key insights immediately, revealing patterns, trends, and relationships that could go unnoticed in traditional data formats. In the age of Big Data, this technique has become essential to extract value from information and guide effective business strategies.
Types of Data Visualizations
As technology advances, visualization techniques have expanded beyond traditional charts, encompassing everything from simple 2D representations to complex 3D models and digital twins.
2D visualizations are the most traditional and various types of dashboards and reports are used. These charts present data clearly and concisely, facilitating the understanding of trends, comparisons, and distributions. Common examples include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, heat maps, treemaps, and scatter diagrams. They are ideal for presenting static data or visual summaries of complex information.


3D visualizations, also known as Visual Analytics, take data representation to a higher level by allowing interaction with data in three dimensions. This type of visualization is especially useful when data has a spatial component or when a more immersive experience is desired to understand dynamic processes.


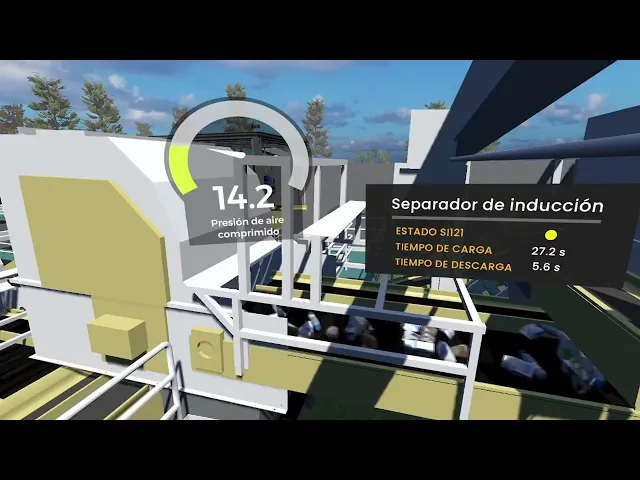
Unlike the previous point, data visualization through a digital twin like TOKII allows you to understand data analysis immersively. This means you can simulate and monitor your factory's operations while seeing data in real-time to facilitate decision-making.
Digital twins allow advanced analyses and visualize results directly on machines while they operate in real-time. This type of visualization not only improves understanding of data but also enhances the ability to respond to problems or opportunities.



The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Data Analysis and Interpretation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are radically transforming how industrial companies analyze and interpret their data. Their ability is limited to analyzing historical data; their true strength lies in their ability to identify complex patterns, predict future outcomes, and, most importantly, adapt to new circumstances.
At IMMERSIA we are applying these technologies in various projects, as we will see in the next section. One of our most interesting solutions is the no-code ML module, designed for companies to apply machine learning algorithms without the need for advanced technical knowledge.
These companies that use our digital twin (TOKII) are capable of generating virtual environments where they can train and test algorithms without interrupting daily activities, optimize resource consumption, or take preventive actions.
The combination of AI and ML with advanced data management and visualization tools not only drives operational efficiency but also transforms the way factories make decisions, shifting from reactivity to proactivity.
Examples of Industrial Digital Twins
Construction and Engineering
ACCIONA wanted to gain a clearer view of the processes at their recycling plant in Palencia. Traditional monitoring made effective data interpretation difficult and limited their ability to optimize processes and make informed decisions.
The digital twin TOKII was implemented with a high level of detail and realistic animations to enhance visualization and understanding of the processes. Additionally, by facilitating the connection with their existing systems like SCADA, they could monitor data in an immersive environment and see their plant in action in real-time.
Thanks to the implementation of TOKII, ACCIONA achieved its goal of having an accurate visualization of what was happening in their plant and recycling processes, improving operational efficiency and enabling quicker and more informed decisions thanks to the visualizations of their established key KPIs in the immersive environment. Furthermore, they also benefited from a significant improvement in collaboration between teams by managing, sharing, and understanding data in a more agile manner.
Machine-Tool Sector
DIMECO has defined the need to have an advanced graphical representation of the HMI (Human-Machine Interface) of their manufacturing lines, as well as the ability to calculate the loop size and speed of production of their manufacturing processes.
To meet these needs, we adapted TOKII to the specific needs of DIMECO, customized to integrate an advanced visualization solution and an integrated simulator. This simulator equipped with advanced technologies such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence allows them to calculate optimal distances and the size of the hole to dig between machines, adapting to different production speeds.
Thanks to the implementation of TOKII, DIMECO has optimized the configuration of its production lines with precise simulations, reducing costs and avoiding unnecessary infrastructure work. Additionally, advanced visualizations have allowed real-time monitoring of production, enhancing both productivity and the customer experience.
Data Analysis Tools for the Industrial Sector
Faced with the challenge of managing an increasing amount of data generated from multiple sources, there is a growing need to know how to choose the right tool. Within the ecosystem of Big Data and Business Intelligence solutions, there are specific software and comprehensive platforms that encompass multiple features.
If you're looking for a comprehensive platform designed especially for the industrial sector, TOKII includes everything necessary to integrate, analyze, manage, and visualize data. Its integration of digital twins, advanced analytics, and real-time visualization makes it an ideal solution for factories looking to optimize critical processes, such as predictive maintenance or real-time resource management.
On the other hand, we find Tableau, a tool that shines in data visualization and creating interactive dashboards. However, Tableau may be less effective in environments where real-time analysis or deep integration with industrial systems, such as SCADA or IoT, is required.
In this same category, we find the famous Power BI, which stands out for its ease of use and integration with systems and its Microsoft ecosystem. The disadvantage is that it is not a tool designed for the industrial sector and falls short in more advanced industrial scenarios.
Qlik stands out for its ability to integrate real-time data and allow detailed analyses in complex industrial environments. However, its steeper learning curve may require additional resources in terms of training or consulting, which could be a limitation for companies with smaller teams.




